The EPR Brains Paradox
The Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen (EPR) paradox in consciousness studies consists of distant correlations between humain brains, sustaining the hypothesis that the brain is a macroscopic quantum processor. Grinberg et al (1994) found the first statistically valid outcomes around the topic and pave the way toward an extended and more holistic view of human consciousness. The results they found consist of transferred potentials, demonstrating brain-to-brain nonlocal EPR correlations and giving credits for the quantum nature of macrolevel brain processes.
Thereafter, many scientists investigated the topic, assuming that microbiological and psychophysical processes might sustain large-scale and nonlocal information processing inside the human brain. One hypothesis is that microtubules inside neurones might be responsible for quantum computation (The Penrose-Hameroff model). The second additional hypothesis focuses on holographic storage and computation in brain electromagnetic interference patterns (The Holonomic Brain Theory). The two hypotheses might be complementary. Indeed, scientific and theoretical investigations are fundamental to understand the anomalies such as nonlocal EPR correlations, that might sustain telepathy as a rational epiphenomenon.
Scientific Research on EPR Correlations
Galdamez, K. M. (2017). Intention at a Distance as a Source of Information Transfer and Wave Function Collapse. 8(1).
Grinberg‐Zylberbaum, J., Delaflor, M., Attie, L., & Goswami, A. (1994). The Einstein‐Podolsky‐Rosen Paradox in the Brain: The Transferred Potential. Physics Essays, 7(4), 422–428. https://doi.org/10.4006/1.3029159
Pizzi, R., Fantasia, A., Gelain, F., Rossetti, D., & Vescovi, A. (2004). Nonlocal correlations between separated neural networks (E. Donkor, A. R. Pirich, & H. E. Brandt, Eds.; p. 107). https://doi.org/10.1117/12.540785
Richards, T. L., Kozak, L., Johnson, L. C., & Standish, L. J. (2005). Replicable Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evidence of Correlated Brain Signals Between Physically and Sensory Isolated Subjects. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 11(6), 955–963. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2005.11.955
Wackermann, J., Seiter, C., Keibel, H., & Walach, H. (2003). Correlations between brain electrical activities of two spatially separated human subjects. Neuroscience Letters, 336(1), 60–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(02)01248-X
Source :
Inter-Brain Synchronization during Social Interaction
Guillaume Dumas1,2,3*, Jacqueline Nadel4, Robert Soussignan5, Jacques Martinerie1,2,3, Line Garnero1,2,3
1 Universite´ Pierre et Marie Curie-Paris 6, Centre de Recherche de l’Institut du Cerveau et de la Moelle e´pinie` re, UMR-S975, Paris, France, 2 Inserm, U975, Paris, France,
3 CNRS, UMR 7225, Paris, France, 4 CNRS, USR 3246, Centre e´motion, Pavillon Cle´rambault, Hoˆ pital de La Salpeˆ trie` re, Paris, France, 5 Centre des Sciences du Gouˆt et de
l’Alimentation, UMR-6265 CNRS, 1324 INRA, U-B, Dijon, France
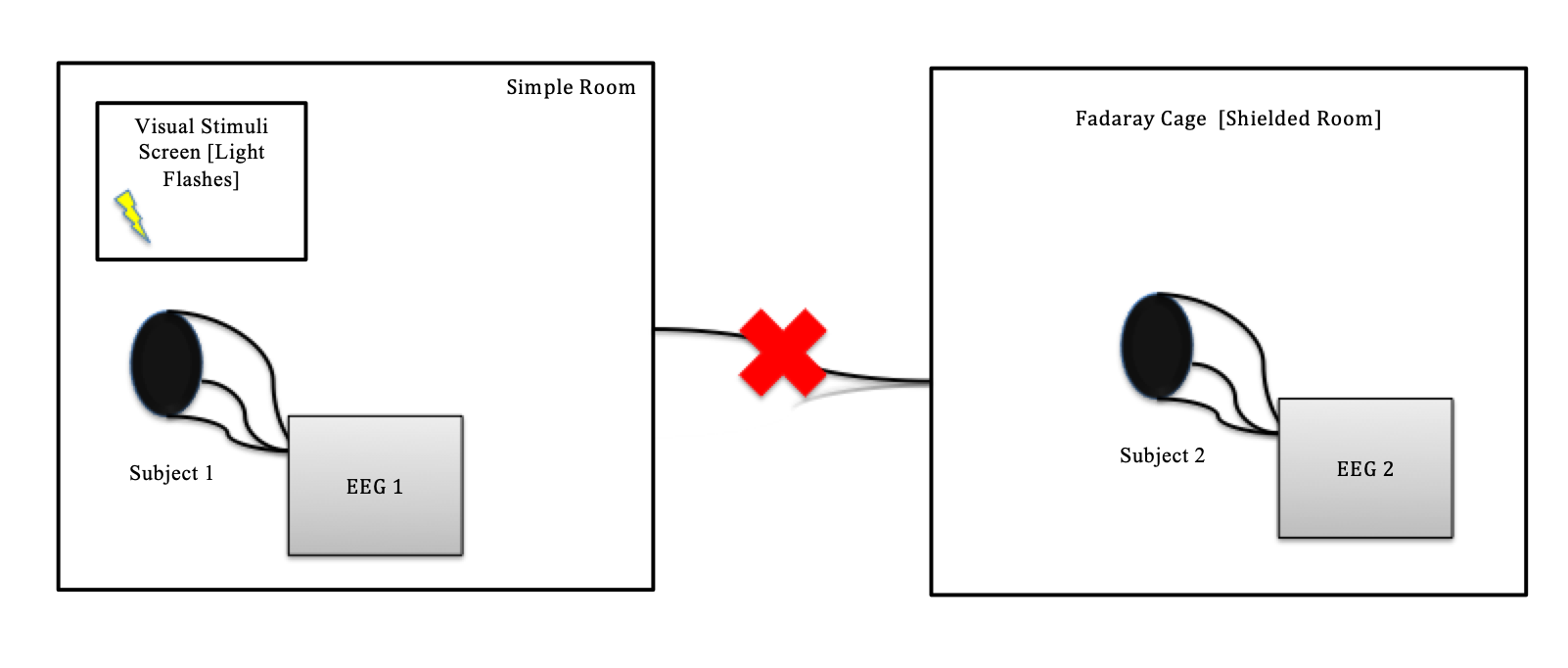
How to investigate the EPR Phenomenon with advanced dual EEG ?
The use of a quantitative EEG mapping procedure with a dual electroencephalography experimental design allows to understand more precisely the EPR paradox in the brain. During the experiment, one participant will be placed in a simple room (obscured, not electromagnetic shielded) or inside a soundproof, magnetic shielded faraday’s cage and the other participant inside the second (or only) faraday’s cage. The subject will be placed, eyes closed, in the faraday’s cage and the practitioner in a simple room (or second Faraday’s cage), in order to avoid electromagnetic interferences between subjects.
Psychic Abilities
Experimental Set-up
It is in between psychophysic and cognitive neurosciences that a sized and adapted scientific experimental protocol can be build. An understanding of what can be expanded consciousness must direct the paradigm, the construction of the experimental set-up based on the hypothesis of non-local occurences and also the possibility to measure it by the means of TMS or dual-EEG.
